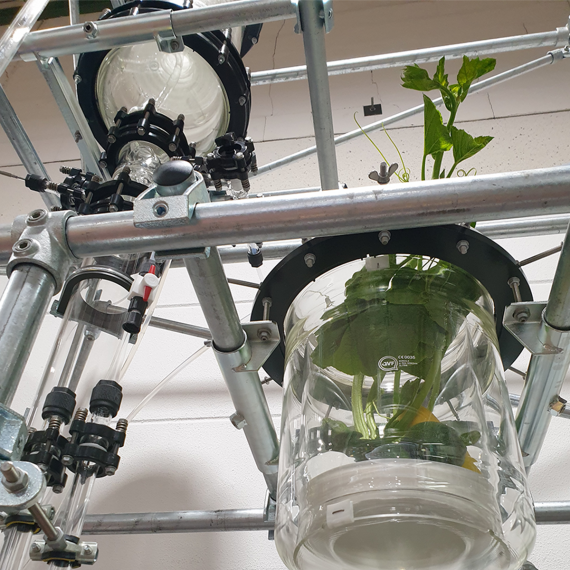
GENERAL INFORMATION
Solid/Liquid extraction or leaching processes have a very long tradition and are widely used in the food, pharmaceutical and chemical industries. The basic idea is to dissolve components out of a solid material with a liquid solvent. Examples in every day’s life are the preparation of coffee or tea dissolving flavors with hot water out of grinded coffee beans or tea leaves. For pharmaceutical applications also other solvents as e.g. alcohols and paraffines or liquified gases as carbon dioxide and propane are commonly used to extract flavors and pharmaceutical ingredients from natural, mainly plant based, material. In the chemical industries almost any solvent incl. the a.m. liquified gases can be found as extracting solvent. In metallurgical applications also acids are commonly used for the leaching process. A suitable solvent does not only provide a high solubility for the component of interest but should also be easy to separate from the extracted component.


.
THE BASIC PROCESS STEPS
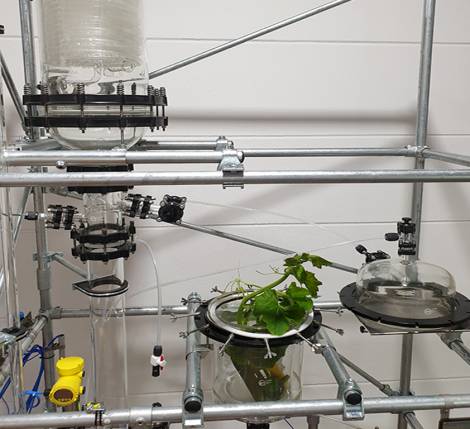
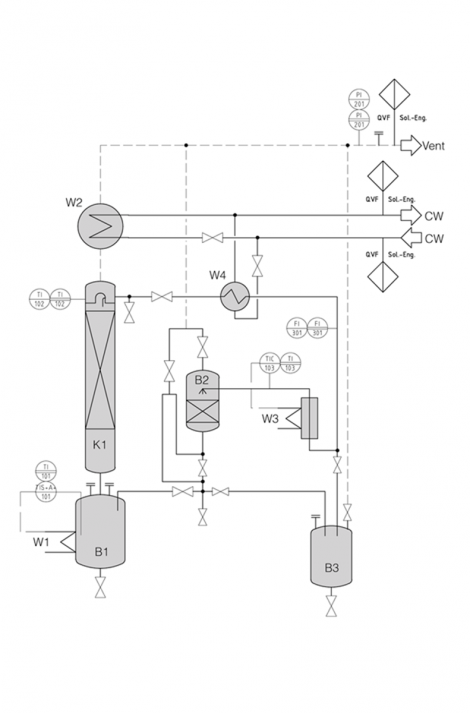
Solid/liquid extraction systems from De Dietrich Process Systems not only enable the extraction process itself but also permit the preparation of the solvent and the preconcentration of the extract. If temperatures sensitive substances are extracted special care has to be taken to avoid elevated temperatures throughout the process. This is very often the case when extracting flavors and ingredients from natural raw material. The complete extraction process can be divided in 3 procedures:
- Preparation of the solvent
- Extraction process itself
- Preconcentration of the extract
The final purification of the extract is commonly realized downstream from the solid/liquid extraction unit.

.
PREPARATION OF THE SOLVENT
The consistence and temperature of the solvent has an important impact on the yield and product quality. One possibility to purify a solvent is its evaporation. This can be realized with electrical heating jackets for spherical vessels or with steam or heat transfer fluids for immersion heater or jacketed vessels. The subsequent condensation of the vapors provides a purified solvent. Its temperature of the condensate depends on the orientation of the condenser. An uprising condensation delivers the solvent at boiling temperature whereas a down coming version at lower temperatures. An additional heat exchanger permits further temperature adjustments of the solvent.

.
EXTRACTION
Prior to the batch extraction the solids have to be charged into the extraction device. This can be a stirred vessel or a receiver with an internal retainer, support or filter for the solids.
The flow of the solvents through the solids is mainly done in 4 different semi-batch modes:
- Trickle bed – trickling of the solvent from the top of the solids towards the bottom of the receiver.
- Underflow extraction – the solids are flooded with solvent passing from the top to the bottom of the receiver.
- Overflow extraction – the solids are flooded with solvent passing from the bottom to the top of the receiver.
- Soxhlet – repeated cycles of filling from the top and draining through the bottom of the receiver.
After the extraction process the solids have to be taken out, the receiver been cleaned and reloaded with fresh solids for the next extraction process. The product of the extraction process is solvent containing the extract and guided into a receiver.


.
PRECONCENTRATION OF THE EXTRACT
In many cases the receiver for the mixture of the solvent with the extract can be used as evaporator for the solvent. This serves during the extraction process to prepare and cycle the solvent. After the extraction process the evaporator serves to preconcentrate the extract. In order to minimize potential thermal degradation of the extract, the evaporation can be carried out under vacuum conditions to reduce the boiling point and hence to reduce the temperature in the evaporator.

.
RANGE OF SOLUTIONS AND SERVICES
Due to the numerous types of solid raw material to be handled, quantities to be processed and the various extraction and leaching liquids used specific technical solutions are the bases for an efficient solid/liquid extraction process. We provide extraction solutions for the following process conditions:
- Volume of solid raw material per batch: 1 - 200l
- Type of solid raw material:
- Plant based material
- Precious metal containing material
- Resins
- Soils and waste
- Type of solvents
- Water
- Organic solvents
- Acids
-
Range of operating conditions
- Extraction temperature 20 – 200°C
- Operating pressure 10 - 1500 mbar abs.

.
YOUR BENEFIT
You can rely on our expertise as manufacturer of a wide range of extraction and leaching equipment and on our process competence for all involved process steps as evaporation, condensation, extraction and filtration. Same for Detailed process knowhow and equipment for up- and downstream purification steps are provided from the same partner: De Dietrich Process Systems – unique partner to manufacture, engineer and built state of the art process equipment.
EXAMPLES OF SOLID/LIQUID EXTRACTORS
Some extractions system with integrated solutions to prepare the solvent and preconcentrate the extract:
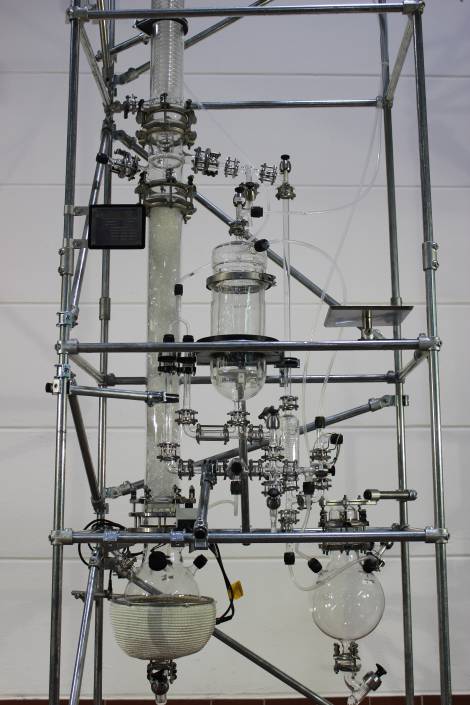
- 1,5l Solid/Liquid-Extractor
- 8l Solid/Liquid-Extractor
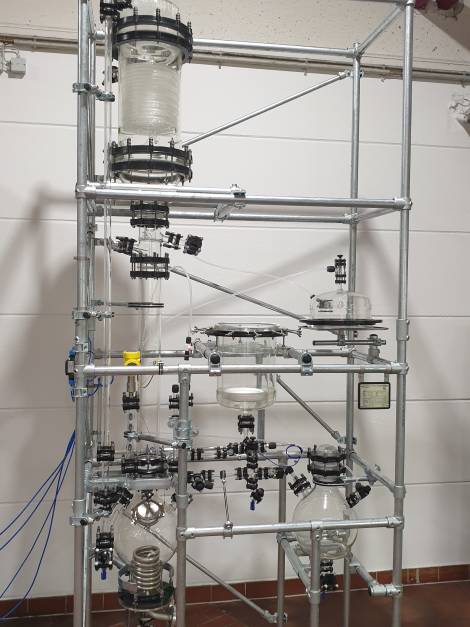
- 12l Jacketed Solid/liquid-Extractor